One of the most frequently asked questions by beginners to engineering simulation is how to learn finite element analysis, and how to use FEA software. This process is not easy, particularly if you want to learn by yourself, not in university. However, with a little motivation and direction, it is achievable.
Let’s start by explaining what FEA is. The finite element analysis is the simulation of any given physical phenomenon using a numerical technique called finite element method (FEM). Engineers use this method to reduce the number of physical prototypes and experiments, and to optimize components in their design phase to develop better products, faster. To understand and learn FEA in depth, this “What is FEA” SimWiki article is a great resource.
This article aims to be a list of valuable resources such as books, papers, validation examples, and more, all of which can help you learn or improve your knowledge about FEA. It is important to note that, in comparison with fluid mechanics problems, FEM software is more commonly used for solid mechanics problems. There are several generic resources and guides available on the Internet, but most of these are based on the one-size-fits-all theory. Firstly, it is important to understand the perspective of the learner, whether the person is coming to FEM as a designer, hobbyist, engineer, mathematician or programmer.
To put your knowledge into practice as soon as you learn FEA, SimScale provides an easy to use, cloud-based platform that provides an interactive interface suitable for FEM simulations. Materials for getting started with SimScale can be found in the blog article “9 Learning Resources to Get You Started with Engineering Simulation“, and the YouTube video “Getting Started with SimScale” is another great starting guide.
For a professional engineer, designer, or hobbyist, the most important thing for learning FEA is to understand the right way to set up a problem. For someone using FEA from this perspective, an FEA software is a black box. Appropriate inputs are applied and corresponding outputs are analyzed to make design decisions. This corresponds to most of the industrial design departments where FEA is used.
With this in mind, it is essential to understand the pre- and post-processing aspects of the process in great detail. Any computer program runs on the philosophy of garbage in, garbage out (GIGO). Thus, if the inputs are not well understood, one will end up dealing with results that don’t make sense physically. In addition, the job description of most engineers or designers does not include debugging the backend FEA program, they are only required to use the results. This is why it’s even more important to be absolutely certain of the accuracy of pre-processing.
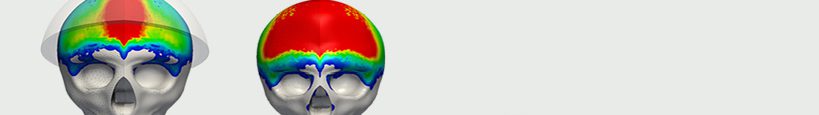
The purpose of a helmet is to protect the person who wears it from a head injury during impact. In this project, the impact of a human skull with and without a helmet was simulated with a nonlinear dynamic analysis. Download this case study to learn more.

One of the first steps is to create a reasonable geometry (or CAD model) that reflects reality as closely as possible. The geometry is generally simplified to create a computationally feasible and efficient model. A convenient way to create CAD models is to use tools like Onshape and Autodesk Fusion 360. Both of these tools are cloud-based and allow free usage. While Onshape currently allows up to 10 models to be stored in private, Autodesk Fusion 360 allows three years of free usage for students, designers, and hobbyists.
It is not always essential to start from the drawing board, however. CAD models can also be found on several public forums. One important word of caution when using CAD models from forums (such as GrabCAD) is to consider the small engravings made by authors. These engravings can significantly affect the mesh creation and need to be removed before using the models. Upon removal of engravings, it is essential to provide appropriate citations as required by GradCAD download licenses. You can find some great tips in this YouTube video: “Preparation of Geometry for FEM Simulation“.
Once the model is created, it needs to be discretized into elements. In other words, the geometry is divided into smaller parts, ensuring that the resulting PDEs are satisfied locally in each of the resulting small elements. For further tips related to meshing for structural problems, take a look at the blog article “How to Mesh Your CAD Model for Structural Analysis”. Similarly, the mesh generation can be found in the meshing documentation pages.
Once the model has been discretized, the parameters need to be provided. The model parameters include defining the relevant materials, constraints like contacts or rigid bodies, and assigning appropriate boundary conditions such as displacement and/or force boundary conditions.
The material can be linear, elastic or hyperelastic when large deformations are involved. In addition, inelastic effects like plasticity or viscoelasticity could also be demonstrated by the material. These aspects need to be taken into consideration and appropriately planned for. Some tips on modeling hyperelastic materials can be found in the following blog articles: “How to Choose a Hyperelastic Material Model” and “Modeling Elastomers Using FEM”. Additional tips on modeling inelastic effects can be found here: “Modeling Inelasticity with SimScale”.
In addition to the previously discussed issues, the material could also undergo damage or fracture. Many commercial software solutions provide limited features for these nonlinearities, and hence appropriate manuals need to be referred to when using such advanced features.
Finally, the boundary conditions need to be provided. In the majority of cases, displacement boundary conditions are preferred to force boundary conditions. This is primarily due to stability issues. In addition, nonlinearity in boundary conditions could arise from aspects like contact. Thus, appropriate contact models need to be assigned to the bodies or surfaces in contact. The state of the art is surface-to-surface contact using the penalty, Lagrange or augmented Lagrangian methods. A more detailed assessment of contact models can be found in the blog article on “Contact Mechanics and Friction”.
As discussed earlier, to learn FEA is not very popular among those who work with fluid mechanics. Fluid mechanics involves the advective/convective terms, which are the first-order terms in the Navier-Stokes equations. The presence of these terms reduces the stability of the solution, primarily at high wave numbers. Hence, the finite-difference methods (FDM) are preferred in fluid mechanics. However, as discussed in our article on “What is FEM?”, novel techniques have been developed as a modus operandi to overcome this problem and continue using FEM and FEM software. Nevertheless, these are two key aspects to consider when setting up a problem related to fluid mechanics. These are whether the flow can be considered laminar, or whether turbulence is important. Some tips and discussions on this issue can be found in the forum topic “Laminar or Turbulence”. If the flow needs to be considered as turbulent, it is vital that the right turbulence models are selected. Again, we recommend seeking further information in the referenced discussion on various turbulence models.
Once the problem parameters have been set up, it is important to choose the appropriate solvers. Parallel computing has become increasingly important in solving large problems of practical importance. In general, there are two main options: direct and iterative solvers. While direct solvers work well for smaller problems up to a million degrees of freedom, iterative solvers are more efficient beyond this. There are several sub-options possible among both classes depending on the platform that is being used for computation. For additional tips on choosing solvers for computing, refer to the blog article “How to Choose a Solver for FEM Problems: Direct or Iterative?“.
The final and most important step to help you learn finite element analysis is to post-process the results. There are several tools available for post-processing, but we recommend the open source tool ParaView. ParaView is also embedded into SimScale to assist with online post-processing. Some tutorials on using ParaView for visualization can be found in the following YouTube tutorials:
In addition, we can also refer you to the blog article “Post-Processing of Aerodynamics with SimScale and ParaView” for more tips on using ParaView online with SimScale.
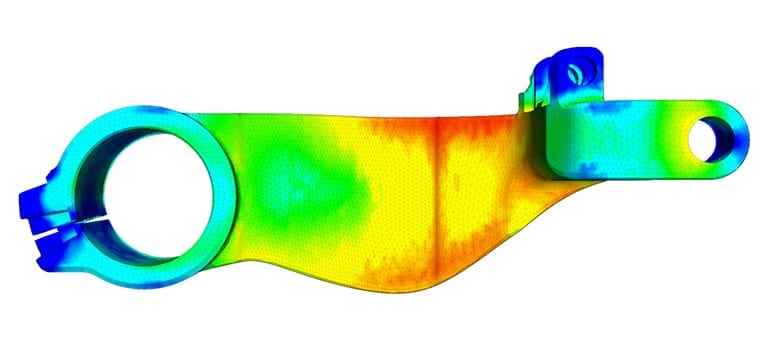
In most cases, people are happy to simply obtain a nice image of the simulation. But what separates a nice picture from a realistic simulation result? Some helpful tips on assessing the results of structural simulations can be found in the article “When Is It Just a Pretty Picture?” and also in this webinar recording: “Tips for a Better Structural Analysis“. It is important to assess whether the simulation results and numbers actually make sense. For example, if the failure threshold for a material is 100 GPa, the stress on the material is 200 GPa, and the resulting picture looks pretty, then there is something wrong with the simulation. In reality, the material should have failed, but it is still carrying loads.
This is where the domain knowledge comes in handy. A concise list of basic books to get a general domain knowledge include:
For the more experienced engineers and designers who would like to get an engineering perspective on finite element analysis, some helpful reads include:
All of the above books discuss linear FEM primarily. There is no one perfect reference book that suits every language and interest. Since nonlinear FEM does require a deeper insight into the topic, it will be discussed further in the upcoming section.
To read more about finite element analysis and the theories supporting it, check out the SimWiki, where you can find more articles related to computer-aided engineering.
This part of the article addresses the interests of programmers, developers, and mathematicians who want to learn finite element analysis. The main interest for those who find themselves in this category is to develop their skills in the finite element method, including the development of new methods, elements, material models, etc. Thus, it is necessary for these learners to completely understand how FEM works. This section will address resources related to the black box.
In the last section, the emphasis was on the pre- and post-processing regimes. In contrast, this section will focus on providing resources related to how FEA works in the background. To learn FEA, you need a solid understanding of the related mathematics, including linear and tensor algebra, differential and integral calculus, complex numbers, etc. In addition, continuum mechanics forms the basis of all mechanical engineering related problems. A thorough understanding of continuum mechanics is a mandatory pre-requisite to understanding and mastering FEA. The two-volume and freely available treatise by Prof. Rohan Abeyaratne on this topic serves as an excellent starting point for this venture.
Another particularly good reference connecting continuum mechanics to finite element analysis is the book “Nonlinear Continuum Mechanics for Finite Element Analysis” by J. Bonet and R. Wood.
In addition, at the very minimum, a basic understanding of functional analysis, variational methods, and tensor calculus is mandatory for most programmers and developers. Of course, for mathematicians who learn FEA, this is their bread and butter, and they should find the material familiar. An excellent book for engineers who want to understand the terminology used in the finite element literature can be found in “Introductory Functional Analysis: With Applications to Boundary Value Problems and Finite Elements” by B. D. Reddy. Some other useful resources with regard to these mathematical preliminaries include:
Moreoever, good repositories of knowledge on linear finite elements and detailed treatment of involved mathematics can be found in:
Once these basic pre-requisites to learn finite element analysis have been completed, there are three more outstanding books and references in the area of nonlinear mechanics:
Each of these texts presents the ideas of nonlinear mechanics in their own unique fashion. There is no one best book here, and learners must adapt to whichever one provides the most familiar notational and mathematical reading.
In addition, in the area of inelastic problems related to plasticity, viscoelasticity or creep, the book “Computational Inelasticity” by J. C. Simo and T. J. R. Hughes has remained an authority for over two decades. The pioneering work of Simo and co-workers remain state of the art in the area of simulation of the inelastic phenomenon.
Moreover, specialized topics—such as using FEA in contact—are examined in detail in separate texts. The mathematical understanding of mixed methods—commonly used in areas like contact mechanics—is by itself a topic of detailed study. A good beginner book for computational contact mechanics is “Introduction to Computational Contact Mechanics” by A. Konyukhov and R. Izi. Two other texts on computational contact mechanics for advanced readers include:
Both the above texts are mathematically intensive and require a thorough understanding of tensor calculus and curvilinear coordinates. Furthermore, reference texts related to the application of FEM in the areas of fluid mechanics and heat transfer include:
Finally, some books of interest to mathematicians include:
Finally, if one intends to write his or her own FEM code to understand the intricacies, two excellent hands-on references include:
More detailed courses to help you learn finite element analysis can be found on several websites including:
As discussed earlier, it is important that the developed methodologies and programs are validated with standard problems. This is what differentiates a pretty picture from an accurate simulation. Some good sources for validation examples include:
In addition, top computational mechanics journals provide an excellent source of information on the current state-of-the-art research in these areas. They also provide validation examples and sources for comparison for problems involving finite element analysis. Some of the top journals in the area of FEA include:
The purpose of this article was to provide you with all the resources you’d need to learn finite element analysis even as a beginner. The more experience you have with FEA software, however, it is important to filter them and find the ones that help improve your own skills. Good luck! It’s a journey worth making!
If you’d like to learn more about the SimScale cloud-based platform and its capabilities for FEA, download this features overview or watch one of our recorded webinars.
Set up your first simulation with SimScale for free by creating a Community account or view our plans. No installation, special hardware, or credit card required.